Meet the Ingredients That Power Retra Rise
Retra Rise is powered by an expertly selected lineup of ingredients, each chosen for its science-backed benefits and role in supporting your overall health.
Below, you will find in-depth scientific detail on the benefits of each ingredient.
Meet the Ingredients That Power Retra Rise
Retra Rise is powered by an expertly selected lineup of ingredients, each chosen for its science-backed benefits and role in supporting your overall health.
Below, you will find in-depth scientific detail on the benefits of each ingredient.

Nattokinase
Nattokinase is a fibrinolytic enzyme derived from fermented soybeans (natto), known for its ability to degrade fibrin and support healthy blood flow. It enhances the body's natural clot-dissolving capacity by increasing plasmin activity and reducing blood viscosity. Clinical studies show it may help lower systolic and diastolic blood pressure and reduce risk of thrombosis by decreasing circulating fibrinogen levels. Nattokinase also modulates inflammatory markers, such as CRP and IL-6, and may improve endothelial function by reducing oxidative stress and supporting nitric oxide bioavailability.

Bitter Melon
Bitter melon contains bioactive compounds including charantin, polypeptide-p, and vicine, which exhibit insulin-mimetic activity and support glucose regulation. It improves glucose uptake by increasing GLUT4 translocation and inhibiting alpha-glucosidase enzymes, thereby reducing postprandial blood sugar spikes. Bitter melon is also a natural source of superoxide dismutases (SODs), enhancing cellular antioxidant defenses and reducing oxidative stress in pancreatic β-cells. Its anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective actions contribute to improved metabolic health, particularly in individuals with insulin resistance or prediabetes. Additionally, bitter melon supports lipid metabolism, reducing triglyceride levels and improving overall cardiometabolic markers.

Lion’s Mane Mushroom
Lion’s Mane is a neurotrophic mushroom known for its ability to stimulate the production of nerve growth factor (NGF), a protein crucial for the survival and regeneration of neurons. Its active compounds—hericenones and erinacines—have been shown to promote neurogenesis and remyelination, enhancing cognitive function, memory, and mood regulation. Clinical studies suggest Lion’s Mane can reduce mild cognitive impairment in aging populations and support neurological recovery post-injury. It also exhibits anti-inflammatory properties by suppressing nitric oxide production and modulating inflammatory cytokines, potentially protecting against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Its adaptogenic qualities also make it useful in reducing anxiety and enhancing mental clarity.
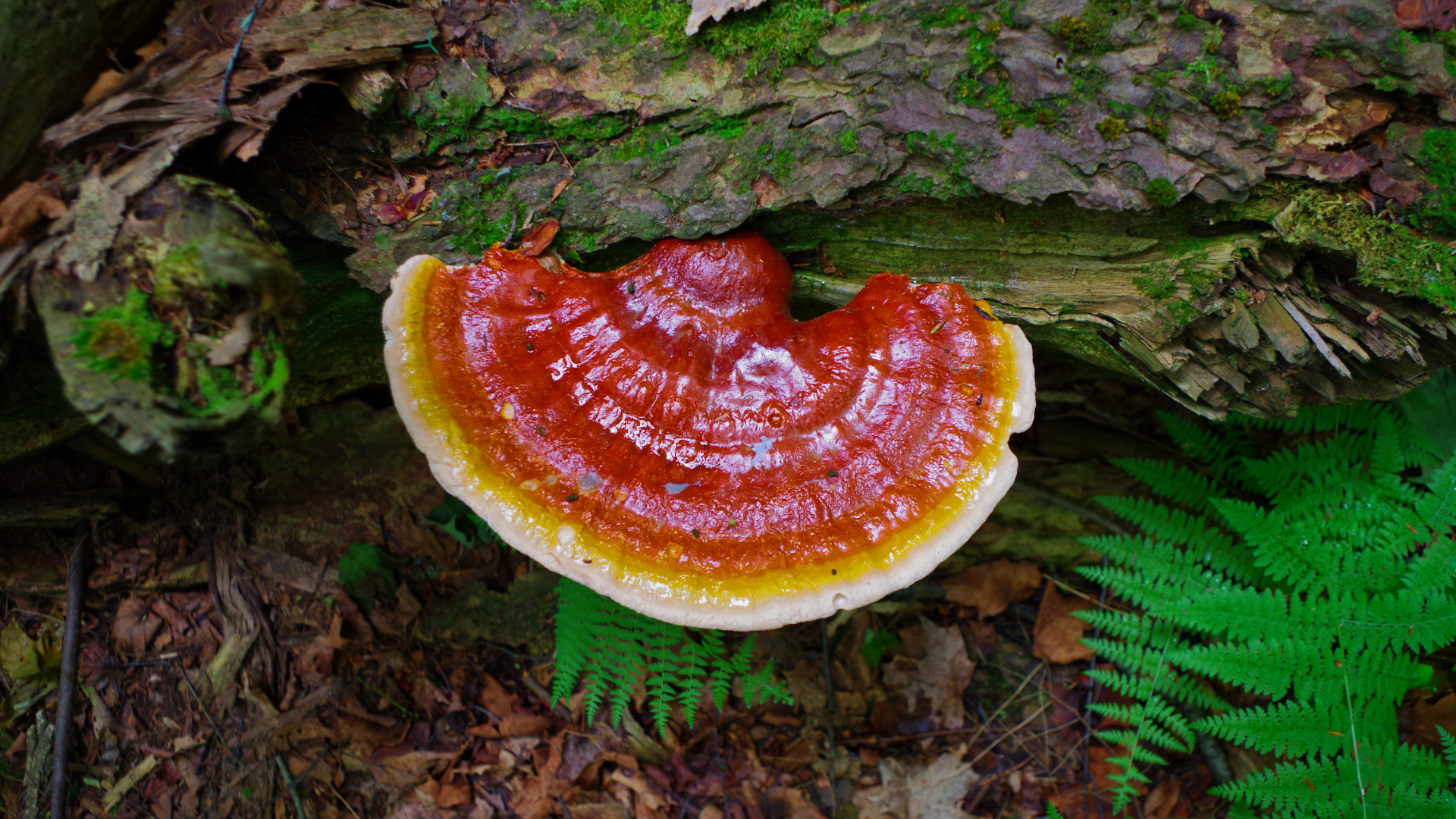

Reishi Mushroom
Reishi is a medicinal mushroom with immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, and adaptogenic properties, attributed primarily to its beta-glucans and triterpenes. It enhances both innate and adaptive immune responses by activating macrophages, dendritic cells, and natural killer (NK) cells, while also regulating T-helper cell activity to reduce autoimmune risk. Reishi has been shown to downregulate pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and TNF-α, supporting reduced systemic inflammation and improved recovery from stress. It also has hepatoprotective effects, supporting liver detoxification and reducing markers of oxidative stress. Additionally, reishi may improve sleep quality and reduce fatigue through modulation of the HPA axis and its sedative effects on the central nervous system.
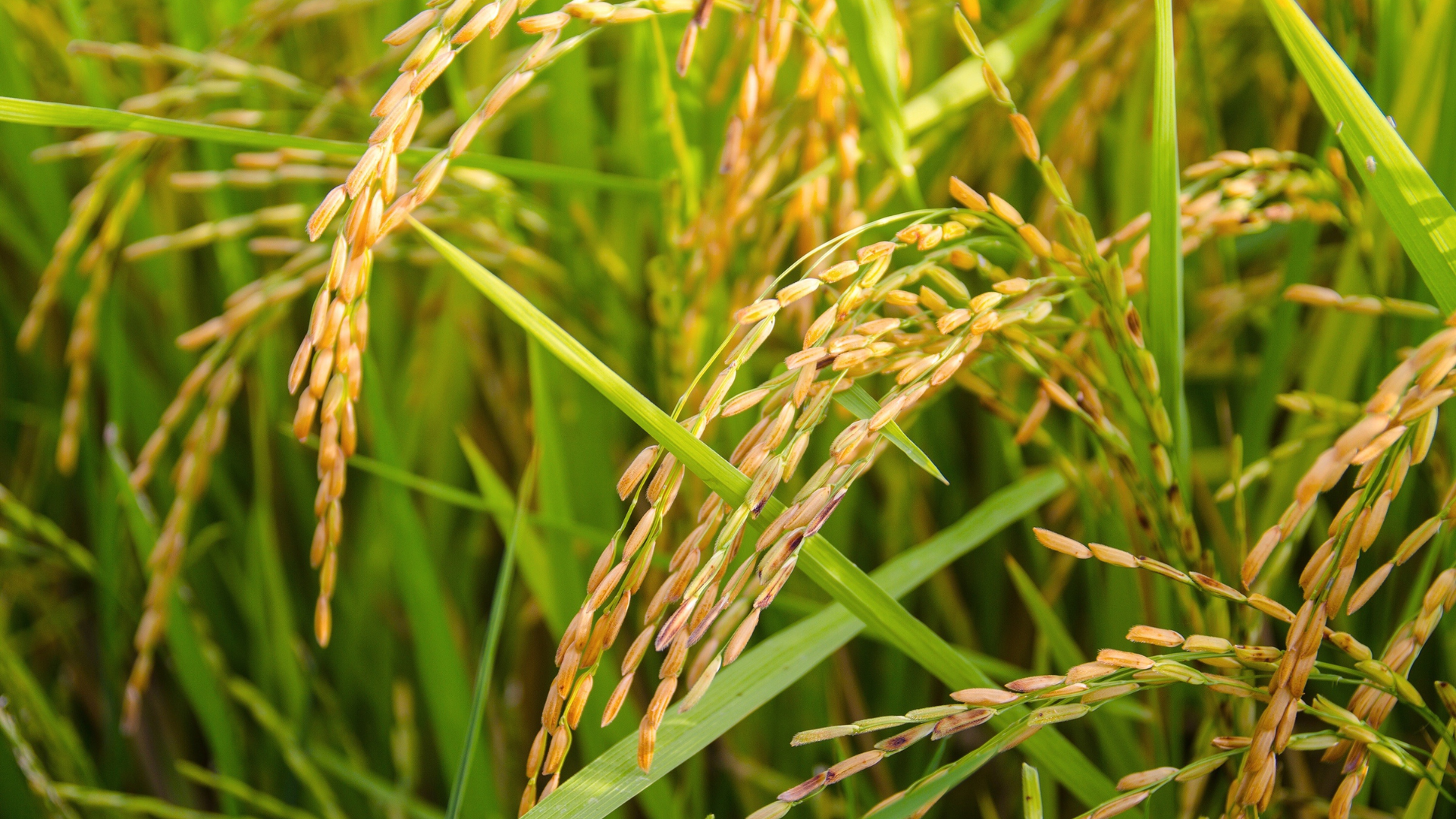

Stabilized Rice Bran
Stabilized rice bran is the nutrient-rich outer layer of the rice grain, preserved using heat treatment to deactivate lipase and prevent rancidity. It contains over 100 biologically active compounds, including tocotrienols, phytosterols, gamma oryzanol, and dietary fiber. Rice bran has been shown to reduce LDL cholesterol, lower postprandial glucose levels, and support healthy lipid metabolism due to its high sterol and fiber content. It also contains ferulic acid and other polyphenols that exert antioxidant effects and modulate inflammatory cytokine expression. In addition to metabolic benefits, rice bran supports gastrointestinal health by feeding beneficial microbiota and improving bowel regularity.
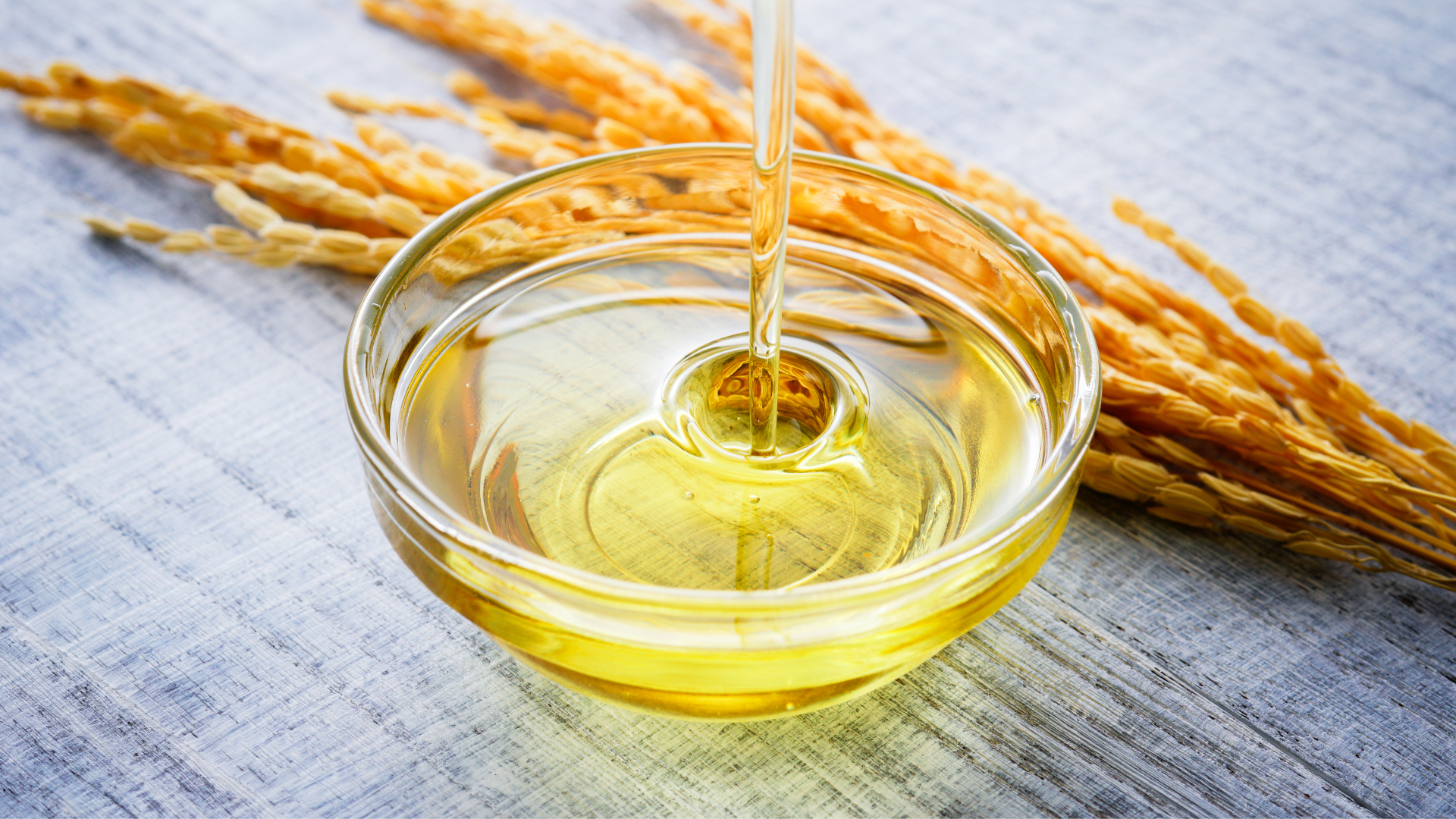

Gamma Oryzanol
Gamma oryzanol is a complex mixture of ferulic acid esters and phytosterols derived from rice bran oil, known for its potent antioxidant and endocrine-modulating effects. It protects cell membranes from lipid peroxidation, stabilizes cholesterol levels by inhibiting intestinal absorption, and supports autonomic nervous system balance. Gamma oryzanol has been studied for its role in improving symptoms of menopausal discomfort, gastric ulcers, and anxiety, potentially due to its regulatory effects on the hypothalamic-pituitary axis. It also influences lipid metabolism and hepatic function, making it beneficial for metabolic health and cardiovascular protection. Additionally, gamma oryzanol exhibits anti-inflammatory and anti-fatigue properties in both animal and human studies.
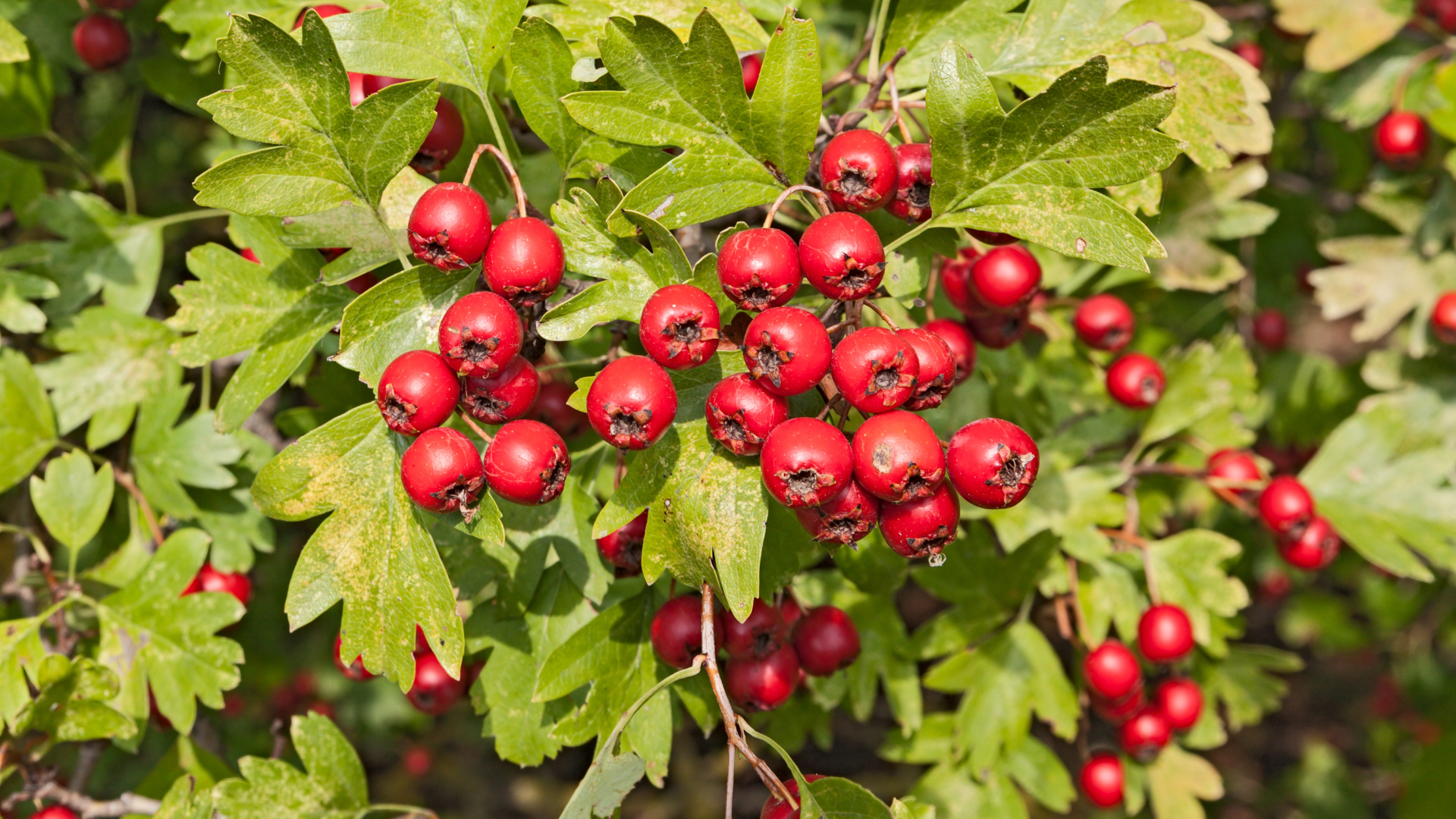

Hawthorn Berry
Hawthorn berry is a traditional cardiotonic agent used to support heart function, vasodilation, and circulatory integrity. It contains oligomeric proanthocyanidins, flavonoids, and vitexin, which improve myocardial contractility and coronary artery blood flow without increasing oxygen demand. Clinical studies have shown hawthorn extract can reduce mild-to-moderate heart failure symptoms, stabilize blood pressure, and normalize arrhythmic patterns. Its vasorelaxant effects are mediated by the modulation of calcium channels and endothelial nitric oxide release. Additionally, hawthorn has mild anxiolytic properties due to GABAergic and serotonin receptor interaction, supporting emotional resilience and stress adaptation.
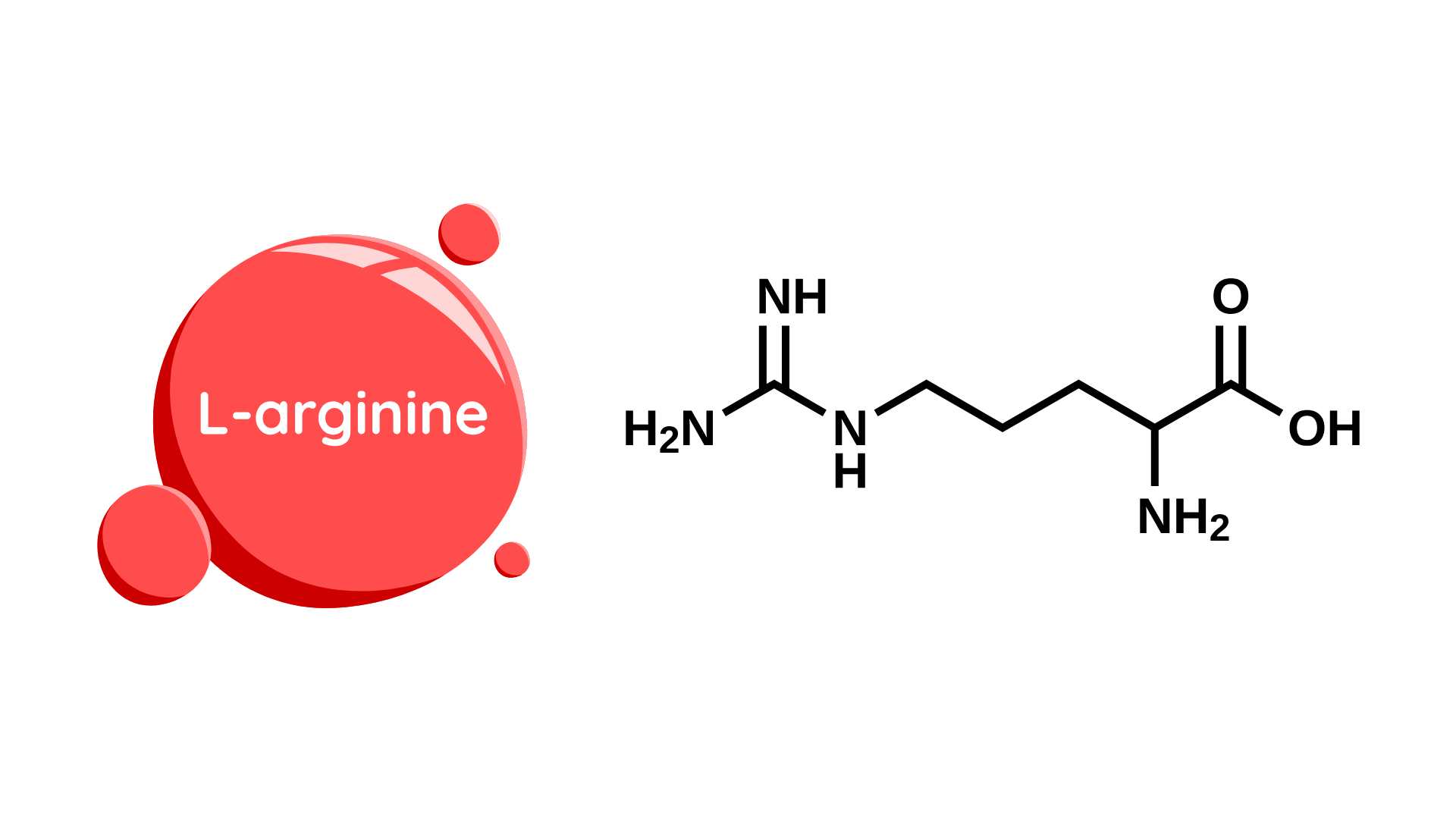
L-Arginine
L-Arginine is a semi-essential amino acid critical for nitric oxide (NO) synthesis via the endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) pathway, leading to vasodilation and enhanced endothelial function. This mechanism supports improved circulation, reduced blood pressure, and enhanced oxygen delivery to tissues—making it especially beneficial for cardiovascular health and athletic performance. It also stimulates the release of growth hormone and insulin, supporting anabolic recovery and glucose metabolism. L-Arginine has been used therapeutically in cases of erectile dysfunction, as it improves penile blood flow via NO-mediated vasodilation. Additionally, it plays a role in immune function by enhancing T-cell proliferation and wound healing.
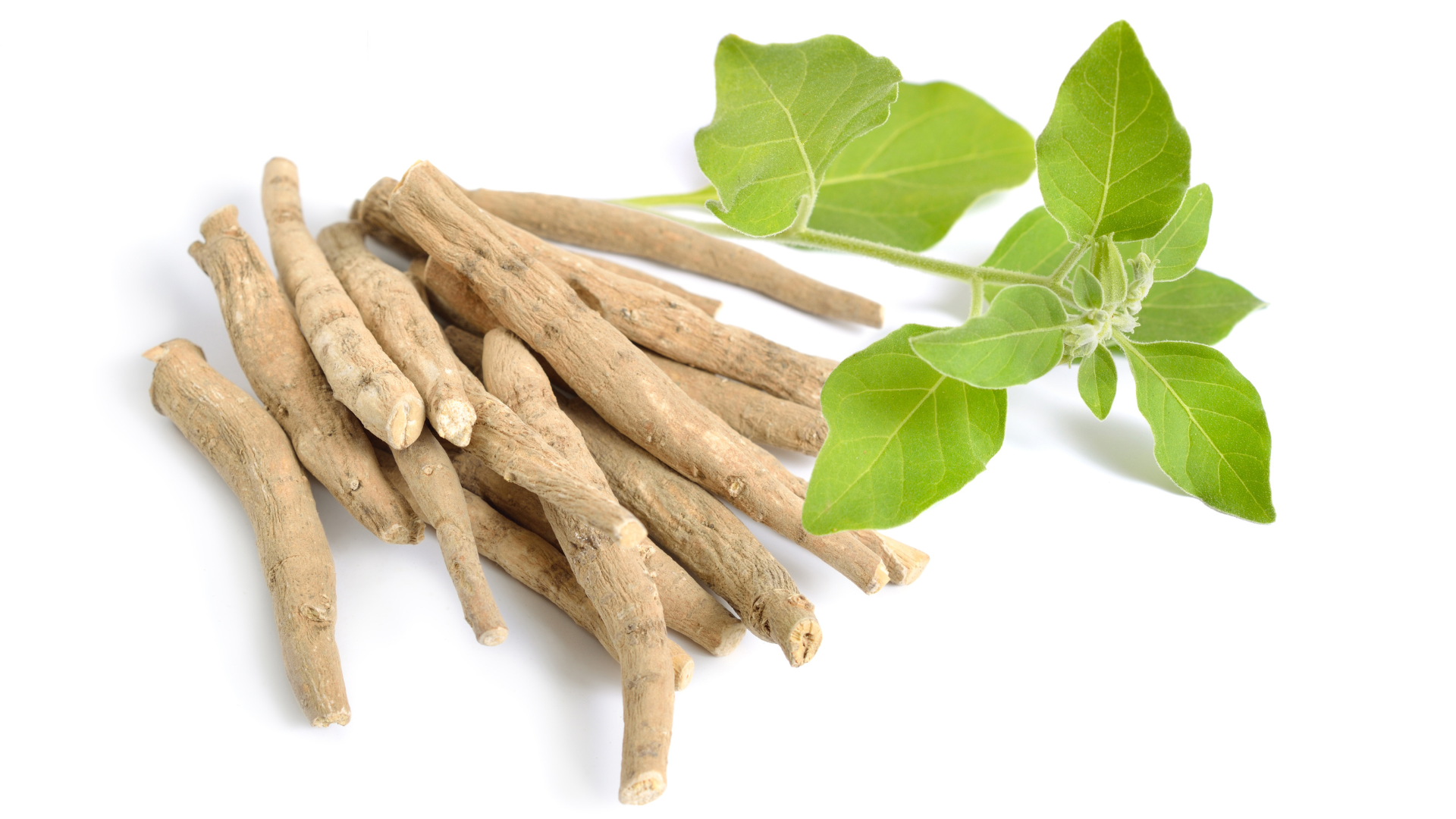

Ashwagandha Root
Ashwagandha is a clinically studied adaptogen that helps modulate the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, reducing elevated cortisol levels and promoting hormonal balance. Its withanolide content supports neuroprotection and improved resistance to physiological stress, making it effective for reducing anxiety, enhancing mood, and improving sleep quality. Research also shows Ashwagandha can improve VO₂ max and muscular strength, indicating benefits for physical performance. Additionally, it has shown efficacy in supporting thyroid health by elevating T3 and T4 levels in subclinical hypothyroidism. Regular intake may enhance cognitive function and reaction time due to its GABA-mimetic properties.
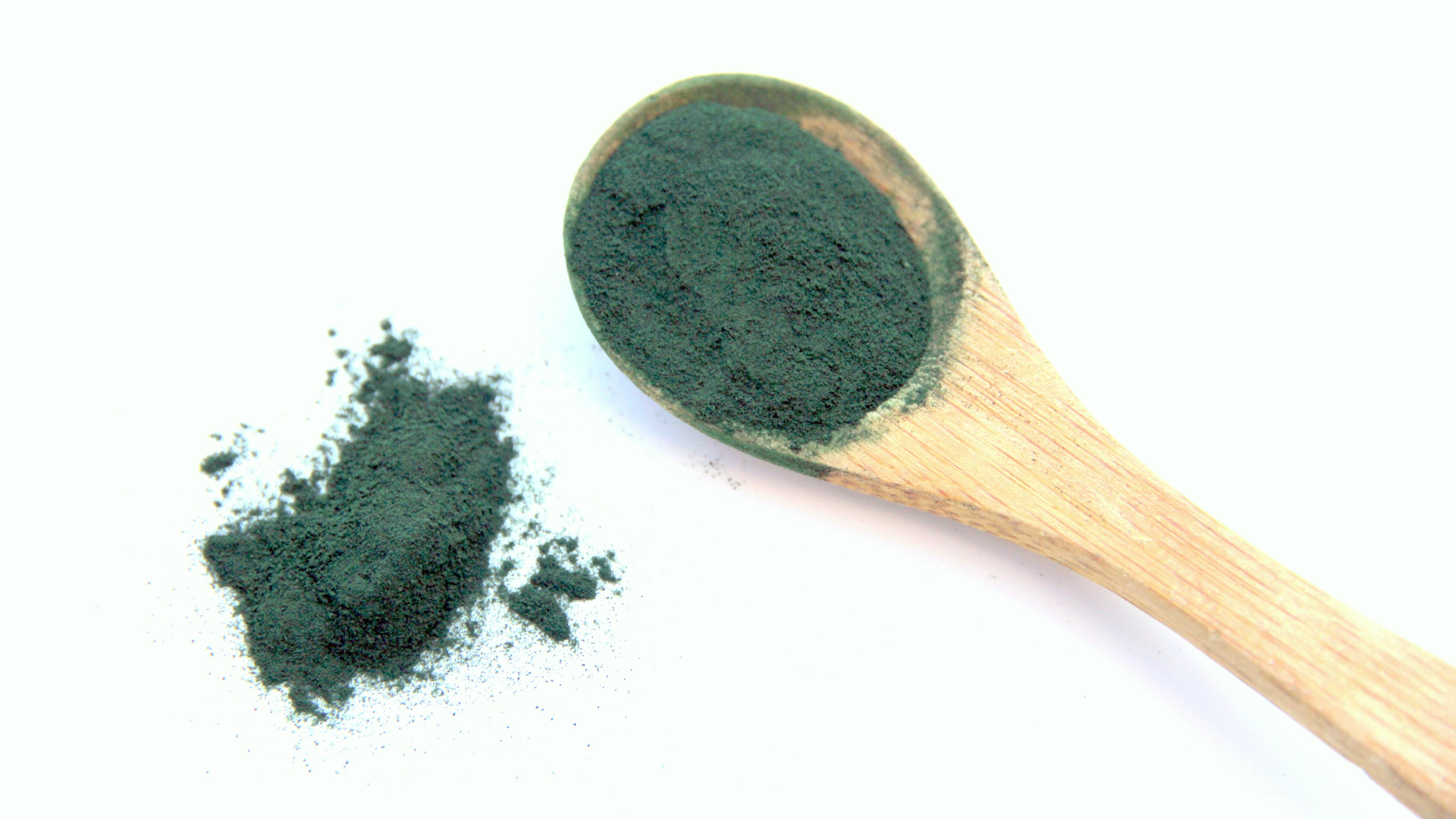

Spirulina
Spirulina is a blue-green cyanobacterium rich in bioavailable protein, B vitamins (especially B12 analogs), phycocyanin, and chlorophyll. It has demonstrated immunomodulatory properties by enhancing natural killer (NK) cell activity and stimulating macrophage function. Spirulina’s antioxidant activity, largely due to phycocyanin and superoxide dismutase (SOD) content, helps neutralize free radicals and reduce lipid peroxidation. It also supports lipid metabolism by reducing serum triglycerides and LDL cholesterol while increasing HDL levels, contributing to cardiovascular health. Its detoxification potential is notable for binding heavy metals and improving liver function markers.
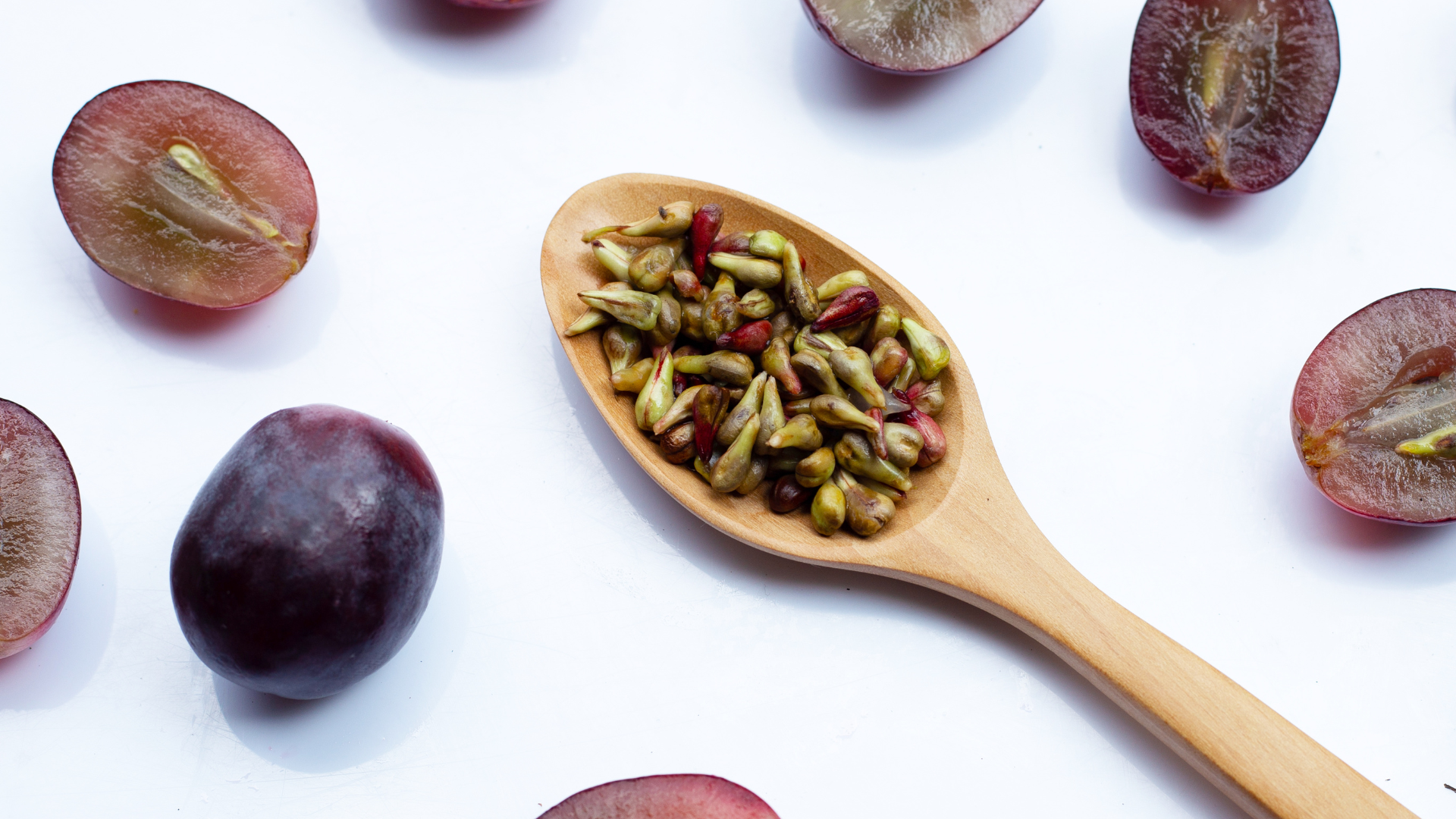

Grape Seed Extract
Grape seed extract is rich in oligomeric proanthocyanidins (OPCs), potent polyphenolic compounds known for their endothelial-protective and anti-inflammatory effects. These compounds scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inhibit lipid peroxidation, offering protection against oxidative stress in vascular and neural tissues. Clinically, grape seed extract has been shown to reduce systolic and diastolic blood pressure and improve microvascular function by stabilizing collagen and elastin in blood vessel walls. It also supports cognitive health by enhancing cerebral blood flow and reducing neuroinflammation. OPCs may further aid in blood sugar control by modulating alpha-glucosidase and improving insulin sensitivity.
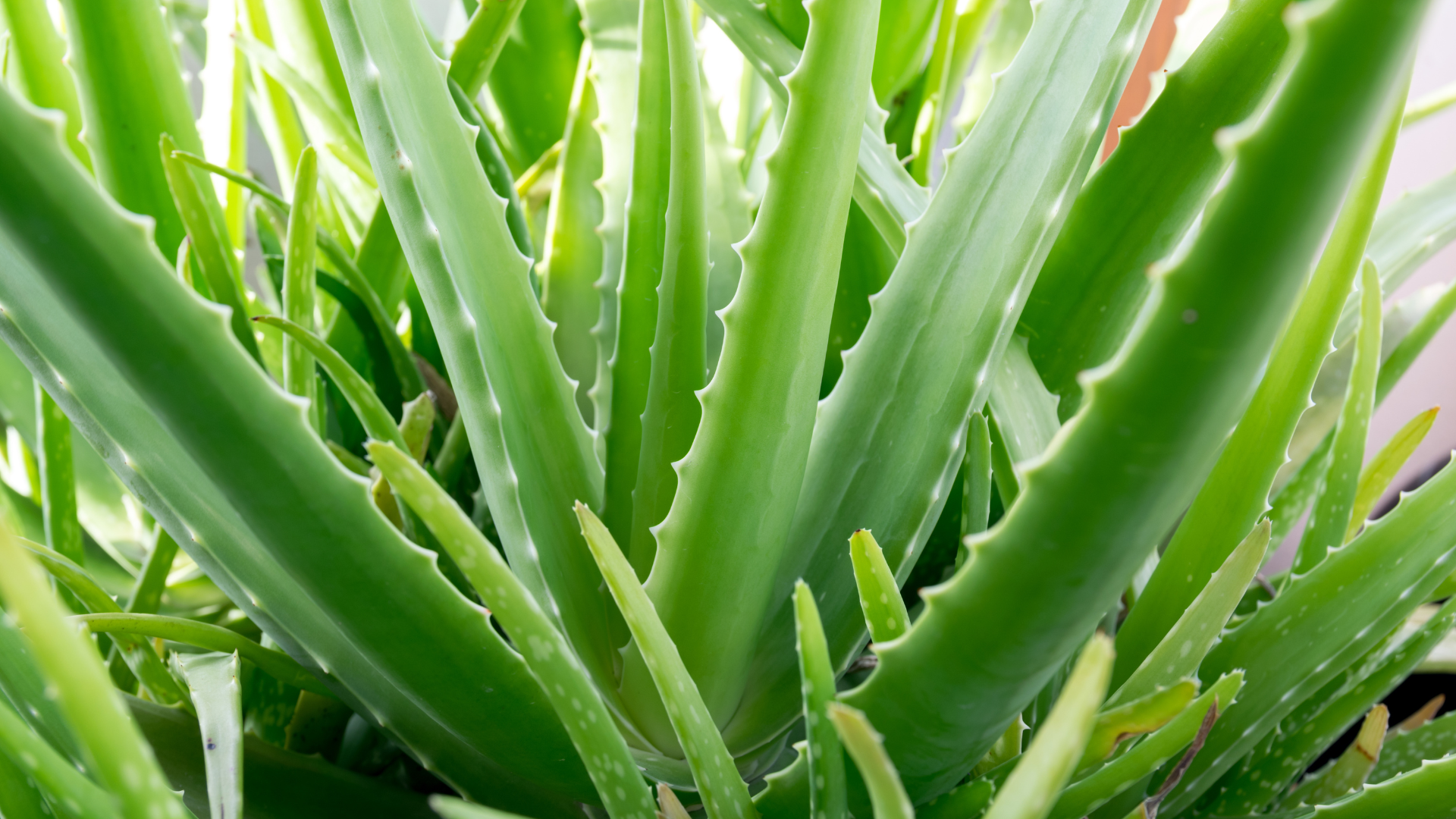

Aloe Vera
Aloe vera gel is a mucilaginous extract from the inner leaf, concentrated 200:1 to preserve its active polysaccharides, including acemannan. These polysaccharides promote epithelial regeneration, making aloe a powerful gastrointestinal healer, effective for soothing inflammation, repairing the intestinal mucosa, and improving nutrient absorption. Aloe also exhibits immunomodulatory effects by activating macrophages and modulating pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β and TNF-α. Its bioactive compounds have shown antimicrobial activity against H. pylori, making it useful in managing dysbiosis. Furthermore, aloe vera enhances skin hydration and supports detoxification by promoting bile flow and liver function.
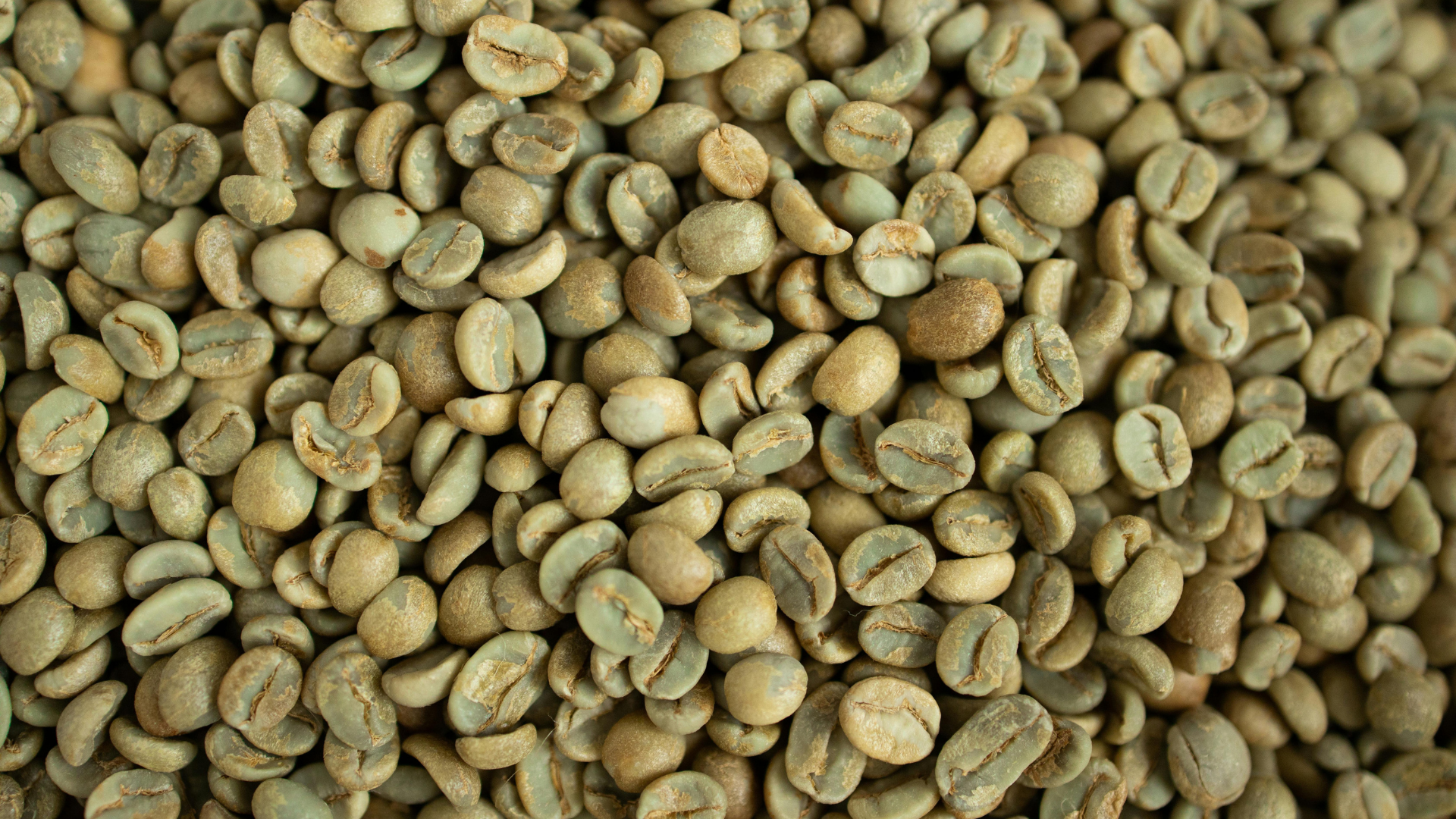

Green Coffee Bean
Natural caffeine sourced from green coffee beans provides a smooth, sustained energy boost by antagonizing adenosine receptors and increasing the release of neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine. Unlike synthetic caffeine, it delivers stimulation without harsh peaks and crashes, thanks to its natural polyphenol matrix, including chlorogenic acids, which also offer antioxidant and metabolic benefits. Chlorogenic acid has been shown to modulate glucose absorption, reduce postprandial blood sugar, and support fat metabolism through hepatic lipid regulation. This combination of gentle stimulation and metabolic support makes it ideal for enhancing cognitive performance, alertness, and physical stamina without overstressing the nervous system.
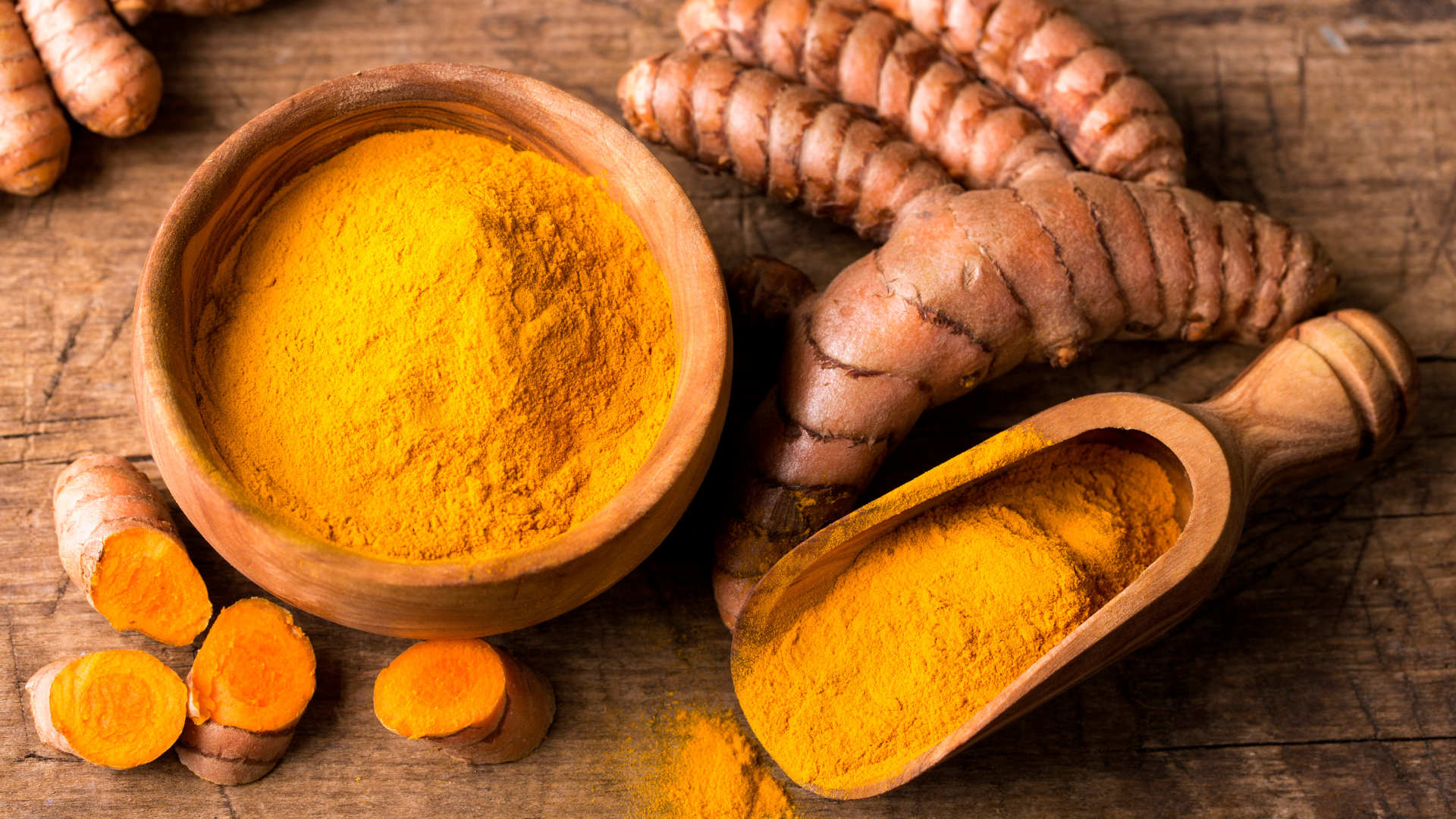

Turmeric Root
Turmeric root contains curcuminoids, particularly curcumin, which possess potent anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and neuroprotective properties. Curcumin inhibits NF-κB and COX-2, key regulators of inflammation, making it effective in managing inflammatory conditions like arthritis and metabolic syndrome. It also scavenges free radicals and upregulates endogenous antioxidants like glutathione and catalase, protecting tissues from oxidative stress. Turmeric enhances brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), supporting cognitive health and resilience against neurodegeneration. Furthermore, it modulates liver enzymes involved in phase II detoxification and improves insulin sensitivity, making it valuable in liver health and glucose regulation.
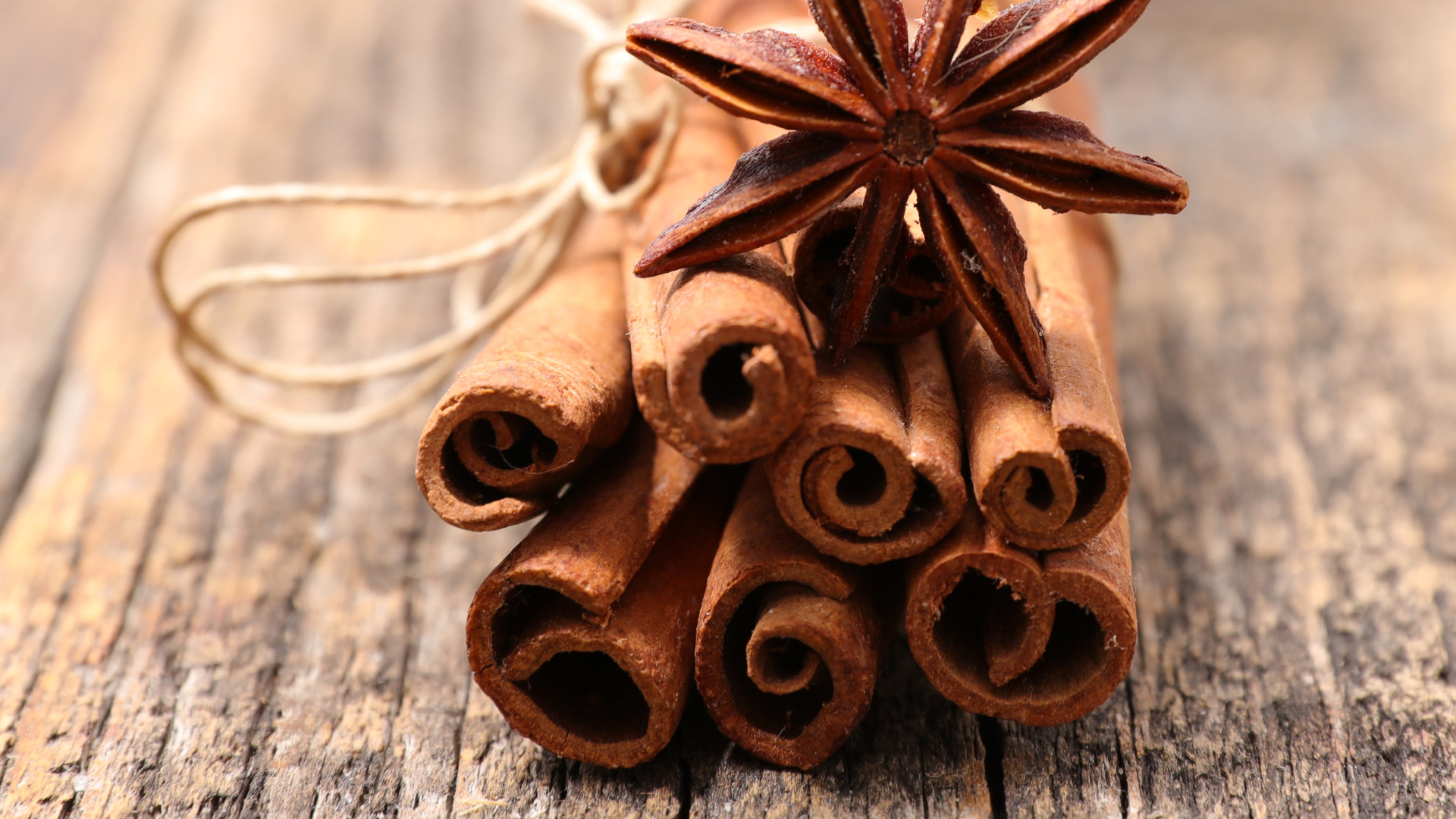

Cinnamon Bark Extract
Cinnamon bark extract provides polyphenols and bioactives like cinnamaldehyde that support glycemic control, lipid metabolism, and antimicrobial activity. It improves insulin receptor sensitivity and enhances glucose uptake by skeletal muscle, mimicking insulin activity. Clinical trials have demonstrated cinnamon's ability to lower fasting glucose, triglycerides, and LDL cholesterol. It also exhibits strong antioxidant activity by inhibiting lipid peroxidation and enhancing enzymatic antioxidant defenses. Additionally, cinnamon modulates gut microbiota and reduces inflammation through NF-κB pathway inhibition.
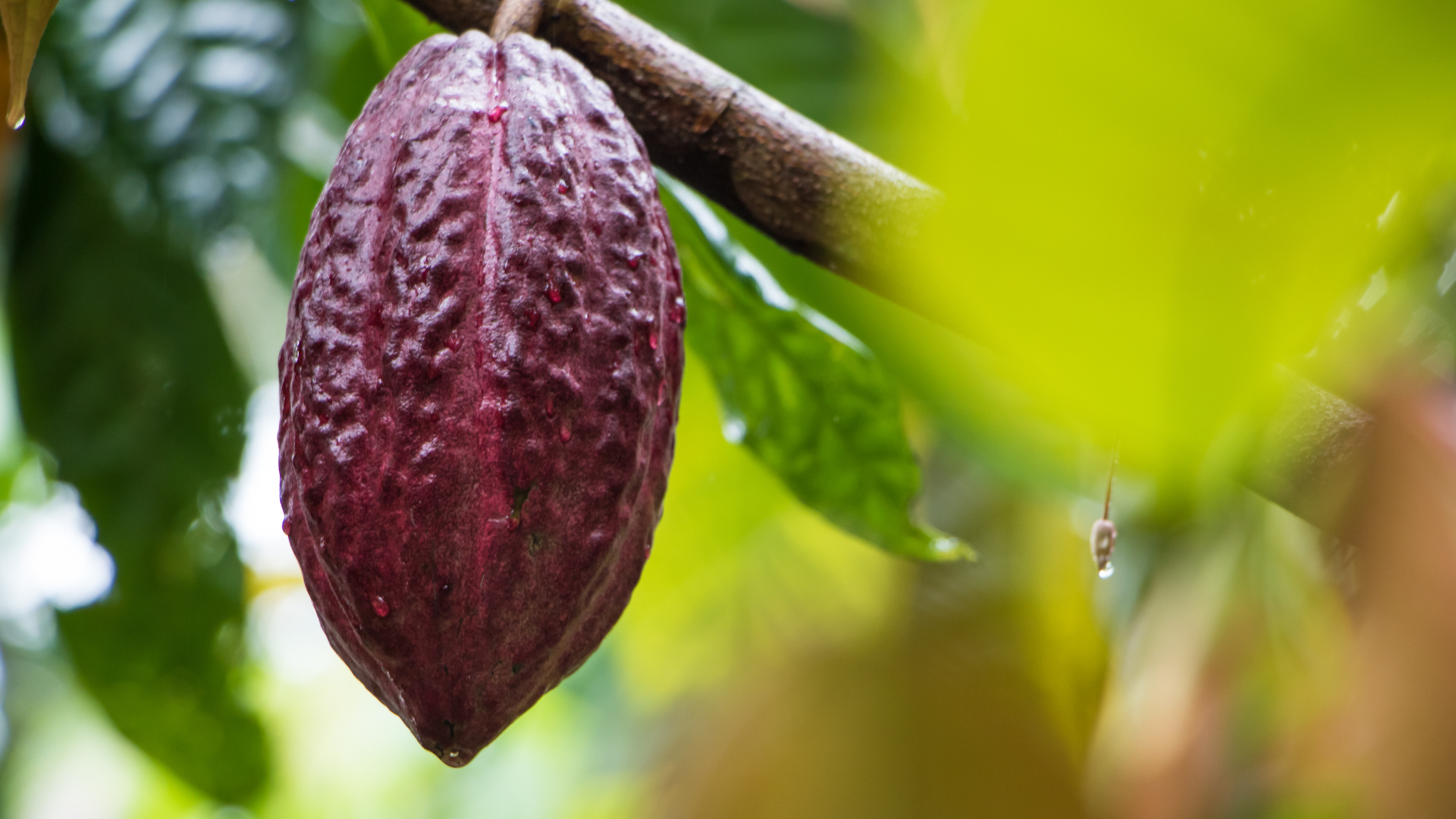

Cacao Powder
Cacao powder contains flavanols, particularly epicatechin, that exert profound antioxidant, vasodilatory, and neuroprotective effects. These compounds enhance nitric oxide production, improve endothelial function, and support healthy blood pressure. Cacao also contains theobromine, a mild methylxanthine that stimulates alertness, enhances mood, and supports bronchial dilation. Cacao polyphenols modulate gut microbiota, reduce LDL oxidation, and have been linked to improved cognitive function through increased cerebral blood flow. Additionally, cacao is rich in magnesium, zinc, and other trace minerals that support energy production and stress regulation.

Pine Bark Extract
Pine bark extract, often standardized to contain oligomeric proanthocyanidins (OPCs), is a potent vascular antioxidant that protects endothelial integrity and reduces systemic inflammation. It enhances nitric oxide synthesis, thereby improving vasodilation, circulation, and blood pressure regulation. Clinically, pine bark extract has been shown to reduce markers of oxidative stress, inhibit platelet aggregation, and support microvascular function—particularly in the brain and extremities. Additionally, it has neuroprotective effects, improving cognitive performance, attention, and working memory by increasing cerebral blood flow. Its anti-inflammatory properties also support joint health, reduce exercise-induced muscle damage, and improve skin elasticity by stabilizing collagen and elastin.
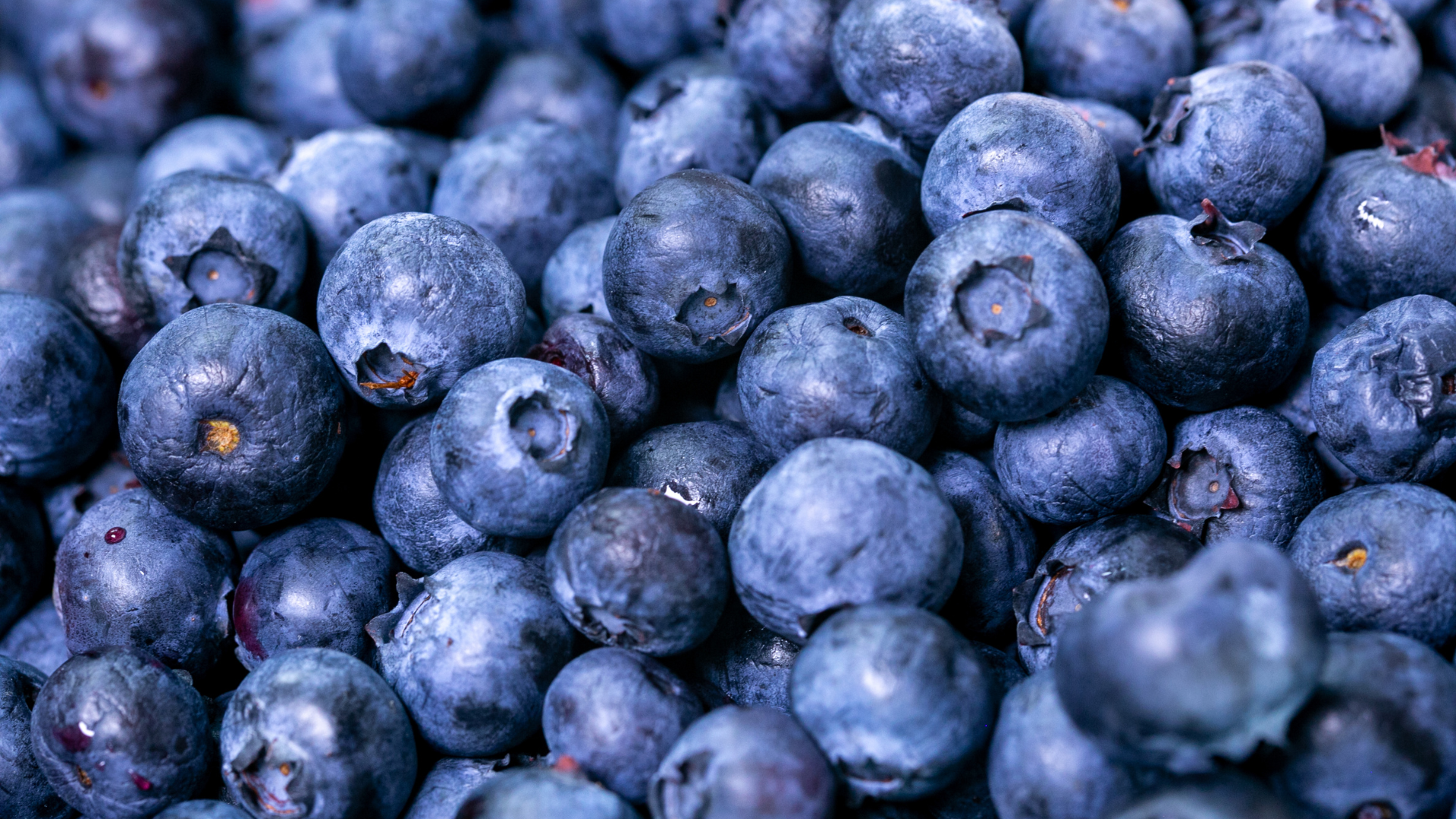

Blueberry
Blueberry extract is rich in anthocyanins, polyphenols known for their neuroprotective and cardioprotective effects. These compounds improve endothelial function by enhancing nitric oxide production and reducing vascular inflammation. In the brain, anthocyanins cross the blood-brain barrier, where they increase BDNF expression, enhance synaptic plasticity, and reduce age-related cognitive decline. Blueberry extract has also been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, support retinal health, and reduce markers of oxidative stress and DNA damage. Its benefits extend to metabolic health by modulating gut microbiota composition, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and reducing systemic inflammation.
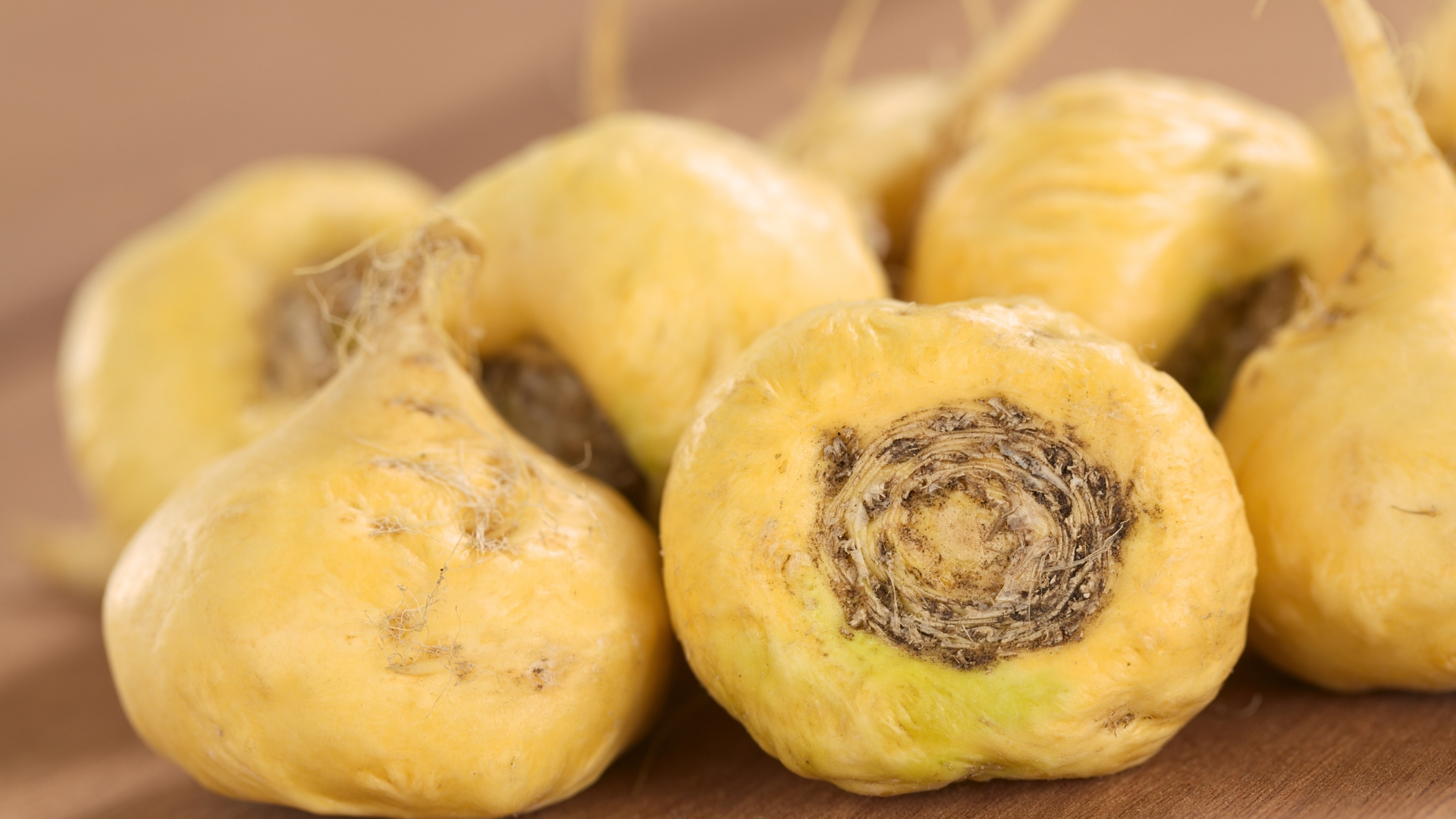

Maca Root
Maca root is a Peruvian adaptogen known for supporting endocrine function and enhancing libido, stamina, and fertility. It contains bioactive compounds such as macamides and macaenes, which influence the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis, promoting hormonal balance without altering serum testosterone or estrogen. Clinical studies have shown Maca can improve sexual desire and reduce symptoms of menopause, such as hot flashes and mood swings. Additionally, Maca exhibits neuroprotective effects, improving learning and memory in animal models, likely due to its antioxidant and mitochondrial-enhancing properties. It may also support bone density and metabolic health by modulating calcium homeostasis and glucose metabolism.

L-Citrulline
L-Citrulline is a non-essential amino acid that serves as a precursor to L-arginine and subsequently nitric oxide (NO), playing a vital role in vascular function and exercise performance. It bypasses hepatic metabolism and is more bioavailable than L-arginine for raising systemic arginine and NO levels. This enhances vasodilation, improves oxygen and nutrient delivery to muscles, and delays onset of muscular fatigue, particularly during high-intensity or endurance exercise. L-Citrulline also supports ammonia clearance through the urea cycle, reducing post-exercise soreness and improving recovery. Its cardiovascular benefits include reduced blood pressure and improved arterial elasticity through endothelial NO modulation.

Goji Berry
Goji berries are nutrient-dense fruits rich in polysaccharides (notably LBP—Lycium barbarum polysaccharides), carotenoids like zeaxanthin, and flavonoids that exert antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and neuroprotective effects. LBP has been shown to enhance immune function by increasing lymphocyte proliferation and macrophage activity, as well as boosting natural killer (NK) cell function. Goji also supports vision health through zeaxanthin’s role in macular protection and oxidative stress reduction in ocular tissues. In clinical trials, daily consumption of goji berry extract has improved mood, fatigue, and overall sense of well-being—potentially by modulating cortisol and serotonin levels. Its hepatoprotective and glucose-stabilizing effects make it especially useful for metabolic and detoxification support.

Pomegranate
Pomegranate is rich in ellagitannins, including punicalagins, which exhibit potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity. These compounds have been shown to inhibit NF-κB and COX-2 pathways, reducing systemic inflammation and oxidative stress. Pomegranate supports cardiovascular health by improving endothelial function, lowering blood pressure, and reducing LDL oxidation. Additionally, pomegranate polyphenols enhance mitochondrial efficiency and have demonstrated neuroprotective effects by reducing amyloid-beta accumulation in models of Alzheimer’s disease. In the gut, pomegranate promotes microbial diversity and increases short-chain fatty acid production, contributing to metabolic and gastrointestinal health.

Chlorella
Chlorella is a green microalga that contains chlorophyll, nucleic acids, beta-carotene, and essential minerals. The “cracked cell” form increases bioavailability by breaking the cell wall that humans cannot digest. It is renowned for its chelation properties, binding to heavy metals like mercury and lead, supporting detoxification through the liver and colon. Chlorella also enhances immune surveillance by increasing levels of immunoglobulin A (IgA) and modulating natural killer (NK) cell activity. It supports cholesterol balance and blood pressure regulation, and its antioxidant capacity—thanks to lutein, chlorophyll, and carotenoids—makes it protective against oxidative stress in tissues and DNA.

Beet Root
Beet root powder provides not only vibrant natural color but also functional value through its rich content of dietary nitrates, betalains, and polyphenols. These compounds help stimulate nitric oxide (NO) production, which supports endothelial function and blood flow. Betalains, the pigments responsible for the red hue, exhibit strong anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective activity. In addition, beet root enhances mitochondrial efficiency and oxygen utilization, making it beneficial for cardiovascular endurance. Although used here primarily as a coloring agent, beet-derived compounds can contribute subtle functional support to circulation and detoxification.

Ginger Root
Ginger is a rhizome with well-established anti-inflammatory, digestive, and circulatory benefits, attributed primarily to bioactives like gingerols and shogaols. These compounds inhibit pro-inflammatory mediators such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes through suppression of COX and LOX pathways, providing relief in inflammatory and pain-related conditions. Ginger enhances gastric motility and accelerates gastric emptying, making it highly effective in managing nausea, bloating, and dyspepsia. It also improves peripheral circulation and supports insulin sensitivity through AMPK activation. As a thermogenic agent, ginger may assist in metabolic function and fat oxidation, making it a valuable component in weight and blood sugar management.

Siberian Ginseng
Siberian ginseng is a well-studied adaptogen that enhances the body’s resistance to physical, emotional, and environmental stress. It functions by modulating the HPA axis, improving adrenal resilience, and normalizing cortisol rhythms, thereby enhancing energy and endurance without overstimulation. Eleutherosides—the key active constituents—have been shown to improve mitochondrial function, oxygen utilization, and glycogen synthesis, contributing to improved physical performance and recovery. Clinically, Siberian ginseng supports cognitive performance under stress and may enhance immune function by stimulating lymphocyte proliferation and increasing interferon activity. Its anti-fatigue and neuroprotective effects make it an excellent adaptogen for high-performance and high-stress lifestyles.

Ancient Sea Salt
Ancient sea salt is a naturally occurring mineral complex harvested from prehistoric seabeds, free from modern pollutants and rich in essential electrolytes. Unlike refined table salt, it retains trace amounts of magnesium, calcium, potassium, zinc, boron, and over 60 additional micronutrients in their naturally chelated ionic forms. These minerals are crucial for maintaining fluid balance, nerve conduction, muscle contraction, and adrenal support, especially in states of dehydration or chronic stress. The sodium in ancient sea salt aids in nutrient transport across cell membranes and supports the production of hydrochloric acid for optimal digestion and nutrient absorption. Its unique mineral profile helps regulate blood pressure, electrolyte status, and mitochondrial hydration, making it far more than a seasoning—it's a foundational support for metabolic and cellular function.

Vitamin C
Vitamin C is a water-soluble antioxidant essential for immune function, collagen synthesis, and protection against oxidative damage. It enhances the proliferation and function of lymphocytes, neutrophils, and natural killer cells, while simultaneously downregulating inflammatory mediators. Ascorbic acid supports the synthesis of carnitine for mitochondrial energy production and serves as a cofactor for prolyl and lysyl hydroxylases—enzymes critical for stabilizing collagen cross-linking in skin, joints, and vascular tissue. It also improves non-heme iron absorption and contributes to skin radiance through its role in melanin inhibition and dermal repair. Chronic deficiency is associated with fatigue, impaired wound healing, and increased oxidative burden.

Soluble Vegetable Fiber
Soluble vegetable fiber is a fermentable prebiotic that feeds beneficial gut bacteria, particularly Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli. These fibers are metabolized into short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, which support colonocyte integrity, reduce intestinal inflammation, and strengthen the gut barrier. SCFAs also play a role in metabolic signaling by modulating GLP-1, improving insulin sensitivity and satiety. Soluble fibers help slow gastric emptying and glucose absorption, reducing postprandial blood sugar spikes and improving nutrient uptake. Additionally, they bind bile acids, promoting cholesterol excretion and supporting cardiovascular health.

Rice Extract
Rice extract offers hypoallergenic, easily digestible plant-based nutrition. It provides a source of amino acids, gamma oryzanol, and trace micronutrients. Its prebiotic and soothing effects on the gastrointestinal tract make it ideal for individuals with food sensitivities or inflammatory bowel conditions. Additionally, rice extract contributes resistant starch and soluble fiber that support microbial diversity in the colon. The phytonutrient matrix within rice extract, rich in ferulic acid and tocotrienols, offers antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that extend beyond the digestive system.

Manganese Gluconate
Manganese is a trace mineral essential for the function of several enzymes, including manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD), a powerful mitochondrial antioxidant. It plays a crucial role in bone development, connective tissue formation, glucose metabolism, and the detoxification of ammonia via arginase. Manganese gluconate offers a highly bioavailable form of this mineral, ensuring effective uptake and cellular delivery. It also supports wound healing, mitochondrial health, and reproductive function by aiding in collagen production and steroid biosynthesis.

Potassium Citrate
Potassium citrate is a highly bioavailable electrolyte that supports neuromuscular function, pH buffering, and cardiovascular health. It plays a vital role in maintaining intracellular fluid balance and blood pressure by counteracting sodium. In the kidneys, it binds to calcium, reducing urinary calcium excretion and the risk of kidney stone formation. Potassium citrate also acts as an alkalinizing agent, helping to reduce metabolic acidosis and support overall acid-base balance—particularly beneficial for individuals on high-protein or acidic diets. It’s essential for proper muscle contraction, nerve conduction, and hydration, especially during physical activity.

Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a lipid-soluble antioxidant that protects cellular membranes from oxidative stress by neutralizing peroxyl radicals. It maintains membrane fluidity, supports immune regulation, and protects low-density lipoprotein (LDL) from oxidation, thereby reducing atherosclerotic risk. Tocopherols and tocotrienols also play a role in gene expression and cell signaling, particularly in immune and neural tissues. Vitamin E’s photoprotective effects benefit skin health by reducing UV-induced free radical damage and inflammation. In combination with other antioxidants like Vitamin C and selenium, it provides synergistic protection against chronic oxidative stress.

Selenium
Selenium, provided in the bioavailable form of L-selenomethionine, is a critical cofactor for several selenoproteins, including glutathione peroxidase and thioredoxin reductase, both of which mitigate oxidative damage and regulate redox homeostasis. It plays a vital role in thyroid hormone metabolism by supporting the conversion of T4 to active T3 and protecting thyroid tissue from autoimmune damage. Selenium is essential for immune defense, enhancing T-cell proliferation, antibody production, and antiviral response. It also supports reproductive health and has been shown to reduce inflammation and DNA damage in high-stress or toxin-exposed individuals.

Vegan Vitamin D3
Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) plays a critical role in calcium and phosphorus metabolism, immune regulation, and gene expression across nearly every cell type. Unlike D2 (ergocalciferol), D3 is the biologically preferred and more potent form, promoting optimal serum 25(OH)D levels. It enhances innate immunity by activating antimicrobial peptides like cathelicidins and defensins, and modulates adaptive immunity by shifting T-helper cells toward a less inflammatory profile. Adequate D3 supports skeletal health, mood balance, and hormonal function, with deficiency linked to depression, autoimmunity, and poor immune resilience. Retra Rise uses a vegan D3 derived from lichen, ensuring compatibility with plant-based lifestyles without compromising bioactivity.

Vitamin A (Retinyl Palmitate)
Vitamin A is essential for vision, skin regeneration, immune defense, and cellular differentiation. In its preformed version, retinyl palmitate is a highly bioavailable storage form that converts to retinol and retinal as needed by the body. It supports epithelial barrier integrity in the skin, gut, and lungs—fortifying innate immune function and promoting mucosal healing. Vitamin A is also vital for the maintenance of visual pigments in retinal photoreceptors and is involved in embryonic development and reproductive health. It acts as a transcriptional regulator by binding to nuclear retinoic acid receptors (RARs), influencing over 500 genes involved in growth, immunity, and inflammation control.

Vitamin B1 (Thiamin HCl)
Thiamin is a water-soluble B-vitamin that serves as a coenzyme (thiamin pyrophosphate) in carbohydrate metabolism, particularly in the decarboxylation of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA. This makes it essential for mitochondrial ATP production and nervous system function. Deficiency can result in fatigue, brain fog, and neurological issues such as peripheral neuropathy or Wernicke’s encephalopathy. Thiamin also supports adrenal function and stress resilience, especially in individuals with high refined carb or alcohol intake, which deplete this nutrient. Supplementation improves mood stability, concentration, and glucose tolerance by optimizing glucose metabolism in neurons.

Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
Riboflavin is integral to redox reactions and energy metabolism through its role as a precursor to flavin mononucleotide (FMN) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), cofactors in the electron transport chain. It supports antioxidant defense by regenerating glutathione and is required for the conversion of B6 and folate into their active forms. Riboflavin improves mitochondrial efficiency, supports detoxification, and helps maintain skin, eye, and mucosal health. Deficiency can present as fatigue, sore throat, cracked lips, and visual disturbances. It is also being studied for its ability to reduce migraine frequency by improving mitochondrial function in neural tissues.

Vitamin B3 (Niacinamide)
Niacinamide is a non-flushing form of vitamin B3 that serves as a precursor to NAD⁺ and NADP⁺, essential coenzymes in cellular energy production, DNA repair, and signaling. It supports metabolism at the mitochondrial level and plays a critical role in sirtuin activation, cellular resilience, and longevity pathways. Niacinamide improves insulin sensitivity, reduces systemic inflammation, and supports neurological health by protecting neurons from oxidative damage and excitotoxicity. It also enhances skin integrity and barrier function by increasing ceramide synthesis and reducing inflammation in acne and hyperpigmentation. B3 is especially important under stress conditions, where NAD⁺ depletion accelerates fatigue and immune dysregulation.

Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
Pantothenic acid is essential for synthesizing coenzyme A (CoA), a central cofactor in the citric acid cycle, fatty acid metabolism, and the synthesis of steroid hormones and neurotransmitters. Its involvement in adrenal hormone production makes it a foundational nutrient for stress resilience and energy production. B5 also supports acetylcholine synthesis, improving memory, focus, and neuromuscular function. Clinically, it has been studied for its role in improving lipid metabolism, reducing LDL cholesterol, and promoting wound healing. Deficiency can manifest as fatigue, irritability, and impaired adrenal function, particularly in high-stress or malnourished individuals.

Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine HCl)
Vitamin B6 is involved in over 100 enzymatic reactions, particularly those related to amino acid metabolism, neurotransmitter synthesis (e.g., serotonin, dopamine, GABA), and homocysteine regulation. Pyridoxal-5-phosphate (P5P), its active form, is crucial for producing mood-stabilizing neurotransmitters and for modulating estrogen metabolism through methylation. B6 is also essential for immune function, hemoglobin synthesis, and reducing inflammation via cytokine modulation. Clinical deficiency has been associated with depression, PMS, fatigue, and impaired glucose tolerance. Supplementation improves cognitive performance, stress management, and hormonal balance, especially in women and individuals with high protein intake.

Vitamin B7 (Biotin)
Biotin acts as a coenzyme in carboxylation reactions involved in gluconeogenesis, fatty acid synthesis, and amino acid catabolism. It supports keratin infrastructure, making it critical for healthy hair, skin, and nails. Biotin also enhances mitochondrial function, supports glucose metabolism, and contributes to gene expression by activating histone biotinylation. Deficiency may lead to brittle nails, hair thinning, skin inflammation, and neurological symptoms. It's especially important for those consuming raw egg whites (which contain avidin), experiencing gut dysbiosis, or taking antibiotics, all of which impair biotin absorption.

Vitamin B9 (Folic Acid)
Folic acid is crucial for one-carbon metabolism, DNA synthesis, and methylation pathways. It supports red blood cell production, neural tube development during pregnancy, and homocysteine regulation, thus reducing cardiovascular risk. In its active form (5-MTHF), folate is involved in neurotransmitter synthesis, especially serotonin and dopamine, contributing to mood regulation and cognitive performance. It also plays a role in detoxification via the methylation of toxins and estrogens. Deficiency is linked to anemia, fatigue, impaired cognition, and elevated homocysteine levels.

Vitamin B12 (Methylcobalamin)
Methylcobalamin is the neurologically active form of B12, essential for DNA synthesis, red blood cell production, and myelin sheath integrity. It plays a key role in converting homocysteine to methionine, a reaction that supports methylation pathways critical for detoxification, mood regulation, and cardiovascular health. B12 is also involved in the synthesis of S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe), a universal methyl donor that influences gene expression and neurotransmitter balance. Deficiency may present as fatigue, neuropathy, brain fog, and mood disturbances, even in the presence of adequate folate. Methylcobalamin is particularly important for vegans, older adults, and individuals with impaired intrinsic factor production.
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions
Retra Rise is an advanced, all-in-one nutritional drink mix that delivers over 50 science-backed ingredients - superfoods, nootropics, adaptogens, antioxidants, vitamins, minerals, and prebiotics - all in one daily scoop.
Retra Rise has a refreshing natural mixed berry flavor with a slightly tart, slightly sweet profile. It's flavored with natural fruit extracts and sweetened with stevia leaf and katemfe fruit... with absolutely no artificial flavors, colors, or sweeteners.
Yes! Retra Rise contains natural caffeine from green coffee beans (the equivalent to a cup of coffee) for clean, sustained energy. There are no synthetic stimulants or harsh crashes.
Absolutely! Retra Rise is designed for daily use and is safe for long-term wellness support. As with any supplement, if you are pregnant, nursing, or under medical supervision, consult your healthcare provider first.


